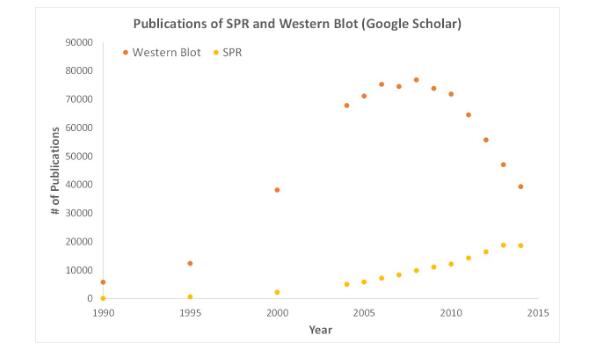
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) causes more than 800,000 deaths worldwide each year. In many developing regions, such as Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, it remains a threat to global health. HBV tends to appear and replicate in human hepatocytes and travels vertically from mother to offspring. In addition, exposure to infected body fluids (ie, sharing needles and sexual intercourse with infected people) can also lead to spread. HBV belongs to the double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) virus of the Hepadnaviridae virus family, and the vaccine has been inoculated for nearly four decades. However, conventional HBV vaccination protocols rely on small hepatitis B surface (SHBs) proteins produced by transfection of S. deresiasia cells in muscle. Notably, SHBs are only one of the three major treatments for HBV antigens, and the literature suggests that there are potential advantages for the remaining two epitopes, the pre-S1 and pre-S2 epitopes. Recently, Dr. Yu-Ching Lee used OpenSPR's local surface plasmon resonance technology to obtain the key data required, and published the article "Interaction of S17 Antibody with Functional Binding Region of Hepatitis B Virus Pre-S2 Epitope" The data obtained with OpenSPR during the study probed the interaction between single-chain variable fragment (scFv) antibodies and pre-S2 epitopes, which may enhance the existing HBV immunotherapy regimen. Summary HBV consists of three major viral envelope proteins, called hepatitis B surface proteins (HBs), which consist of 226 amino acid residues of small hepatitis B surface protein (SHBs) and 281 residual intermediate hepatitis B surfaces. Proteins (MHBs) and 400 residual large hepatitis B surface proteins (LHBs). The traditional vaccination program was developed in the 1980s as a muscle tissue surrounding SHBs in which the transfected yeast cells are the makers of the antigen and subsequently configured as commercial immunotherapeutics. However, the number of non-responders after vaccination is high, which is why it is necessary to find more effective methods of immunoprotection. The article shows that the use of MHBs and LHBs (pre-S1 and pre-S2 epitopes, respectively) in immunotherapy has proven to be an effective prophylactic vaccination regimen in a murine model. Previous studies have also shown that the introduction of pre-S1/S epitopes can also provide effective intervention for more persistent HBV infection. Specifically, the pre-S2 epitope is considered to be a major regulator of hepatitis B virus on hepatocytes and a marker of HB virus invading liver cells. Notably, exposure of the patient to the pre-S2 epitope elicited a higher immune response than the other epitopes described above; residues 123-145 of the polypeptide were notorious for their association with effective neutralization. In this way, the interaction of pre-S2 epitopes with engineered antibodies has become a popular study by immunologists. In this article, the researchers used phage surface rendering techniques to isolate human scFv from HBV patients, followed by selection of major candidates for further analysis of pre-S2 epitopes by ELISA and Western Blots. After flow cytometry and immunocytochemical staining of scFv antibodies, S17 was used for computer simulation and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) detection. analysis The results of surface plasmon resonance studies indicate that scFv S17 is a very strong neutralizing agent for pre-S2 epitopes found on the envelope of HBV virus. It is therefore important to note that the combination of intact IgG molecular structures may increase affinity. OpenSPR help of this study OpenSPR has the characteristics of simple operation, no influence on temperature and buffer refractive index, fast result, stable and sensitive detection. This study used OpenSPR surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technology to quickly determine pre-S2 epitope and scFv. Interaction between antibodies S17. The pre-S2 peptide was immobilized on a streptavidin sensor and subjected to an antibody-antigen reaction experiment on the OpenSPR system. Using OpenSPR, the authors were able to determine the kinetic data (binding and dissociation rate constants, equilibrium constants and affinities) of the interaction between the S17 antibody and the immobilized pre-S2 epitope. The SPR binding curve shows that S17 is effective in interacting with pre-S2, and quantitative data from this experiment indicates an equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) of 4.2 x 10 -8 M. The results produced by this study indicate that the scFv S17 antibody can serve as an effective immunotherapeutic agent by targeting the HBV pre-S2 epitope and can be converted to an improved vaccination regimen for HBV infection. By using OpenSPR, researchers can get SPR data from their own work platforms, which helps them speed up research and publish their findings faster. SPR is an unlabeled detection technology that allows researchers to quantify the binding between two biomolecules. The SPR technique allows us to determine the interactions of kon, koff and KD, and provides a deeper understanding of the interactions between molecules than other techniques that only provide endpoint measurements, such as pull-down experiments. SPR is not only necessary for publishing articles, but also necessary for the development of many medical and medical research fields. As shown in the following figure, the number of articles published by SPR data has increased significantly in recent years. Scientific publications involving SPR have increased drastically over the years. SPR has become fundamental for publications while traditional techniques like Western Blots are becoming less important OpenSPR is a user-friendly and low-maintenance, low-tech threshold for next-generation SPR solutions that are currently used by hundreds of researchers. With LSPR technology at your fingertips, you can get the quality data you need while speeding up your research and publishing! Advantages of Nicoya OpenSPR Molecular Interaction in the Study of Hepatitis B Vaccination Program: • Easy to operate - 1 hour to control; • Complete kinetic parameter detection - Ka, Kd, ​​KD; • High efficiency---loading, results, one-click analysis, results in 10min, complete kinetic test results in 1-2h; • High precision – detection is not affected by temperature and buffer refractive index; • No need for dedicated correction channels – negligible bulk effects; Disposable Face Mask,3-layer Disposable Face cover,Anti Dust Face Cover,Kid Disposable Face Mask Dongguan Keyutai Mask Co., Ltd. , https://www.maskkytai.com